Understanding the Electronegativity Trend Google Trends: A Deep Dive into
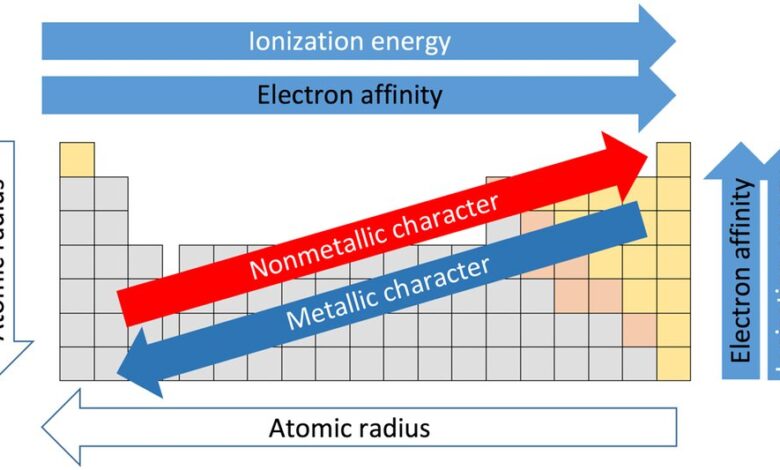
Table of Contents
The Electronegativity Trend Google Trends is a fascinating concept that helps us understand how atoms behave when they form bonds. When you search for “electronegativity trendgoogle trend,” you’ll discover how the electronegativity of elements changes across the periodic table. Electronegativity refers to an atom’s ability to attract electrons, and this ability varies depending on the element’s position in the periodic table. Understanding this trend can be helpful for students, chemistry enthusiasts, and anyone curious about how atoms interact.
As you explore the electronegativity trend on Google Trends, you’ll notice that certain patterns emerge. For example, elements on the right side of the periodic table, like fluorine and oxygen, tend to have higher electronegativities, meaning they attract electrons more strongly. On the other hand, elements on the left side, like sodium and potassium, have lower electronegativities. This trend helps us predict how different elements will behave in chemical reactions and how they form bonds with other atoms.
What is the Electronegativity Trend? Understanding Google Trends in Chemistry
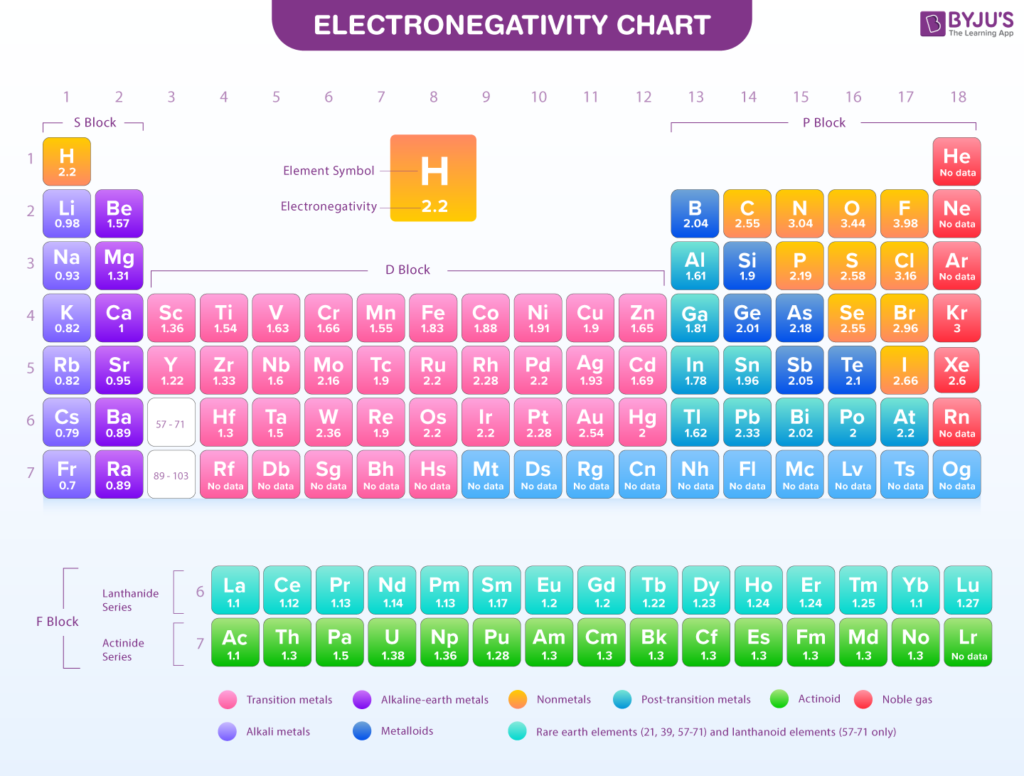
Electronegativity is a term used in chemistry to describe an atom’s ability to attract electrons when forming a bond. The electronegativity trend refers to how this ability changes as you move across the periodic table. If you’re interested in how this trend works, you can use Google Trends to track its popularity over time.
Electronegativity values increase as you move from left to right across a period in the periodic table. Elements on the right side, like fluorine and oxygen, have higher electronegativity values. These elements pull electrons closer to themselves when they form bonds. On the other hand, elements on the left, like sodium and potassium, have lower electronegativity and don’t attract electrons as strongly.
In chemistry, understanding this trend helps us predict how atoms will bond with each other. For example, if two elements with very different electronegativity values form a bond, one element will attract the shared electrons more strongly, creating a polar bond. If the electronegativity difference is large enough, the bond might even become ionic.
How Does Electronegativity Change Across the Periodic Table? Insights from Google Trends
The electronegativity trend shows clear patterns when you examine the periodic table. As you move from left to right across a period, the electronegativity of elements increases. This is because the atoms become smaller and the positive charge from the nucleus attracts the shared electrons more strongly.
On the other hand, as you move down a group, electronegativity decreases. This happens because the atoms get larger, and the nucleus has a weaker pull on the electrons in the outer shell. Therefore, atoms at the top right of the periodic table have the highest electronegativity, while those at the bottom left have the lowest.
Exploring the Role of Electronegativity in Chemical Bonds: Trends and Patterns
In chemistry, understanding electronegativity helps explain why certain chemical bonds are stronger or weaker. Atoms that have similar electronegativity values will form a nonpolar covalent bond, where the electrons are shared equally. However, when there is a large difference in electronegativity, the electrons are shared unequally, resulting in a polar covalent bond.
For example, in a molecule like hydrogen chloride (HCl), chlorine has a higher electronegativity than hydrogen, so it pulls the shared electrons closer to itself. This unequal sharing creates a partial negative charge on the chlorine atom and a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom.
Why is the Electronegativity Trend Important for Chemistry? A Google Trend Perspective
Understanding the electronegativity trend is crucial for predicting how atoms will interact in chemical reactions. If you know the electronegativity of the elements involved, you can predict whether the bond formed will be nonpolar, polar, or ionic. This information is essential for chemists when designing experiments and understanding reactions.
Google Trends shows that people are very interested in how electronegativity affects chemical bonding. This trend is a reflection of how important it is to understand atomic behavior in science.
The Rise of Electronegativity in the Periodic Table: What Google Trends Reveals

Using Google Trends, we can track how the interest in electronegativity has evolved. Over time, more and more students and researchers are looking for information about electronegativity.
Subheading (H3): Tracking Electronegativity in the Periodic Table
- Electronegativity increases as you move from left to right across a period
- It decreases as you move down a group
- The highest electronegativity elements are on the top right
- The lowest electronegativity elements are on the bottom left
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the electronegativity trend is very important for learning how atoms bond and react in chemistry. By knowing which atoms attract electrons more strongly, we can predict whether a bond will be strong or weak.
With tools like Google Trends, we can see how popular topics like electronegativity trendgoogle trend are becoming. This shows that people are more interested in learning about these science topics, and it helps educators stay updated on what students are curious about.
FAQs
Q: What is electronegativity?
A: Electronegativity is a measure of how strongly an atom can pull electrons toward itself when it forms a bond with another atom.
Q: Why does electronegativity increase across a period?
A: Electronegativity increases across a period because the atoms get smaller and the nucleus pulls electrons more strongly.
Q: What happens when electronegativity is very different in a bond?
A: When electronegativity is very different, the electrons are not shared equally, creating a polar bond or even an ionic bond if the difference is large enough.
Q: How does electronegativity change down a group?
A: As you move down a group on the periodic table, electronegativity decreases because the atoms get larger and the nucleus has a weaker pull on electrons.
Q: How can Google Trends help with electronegativity?
A: Google Trends can show how often people search for electronegativity topics, helping us understand its importance and popularity in science education.